Applications
What should I do with all of this clean power?
Data Center
Electrolyzer
Resistive Heater
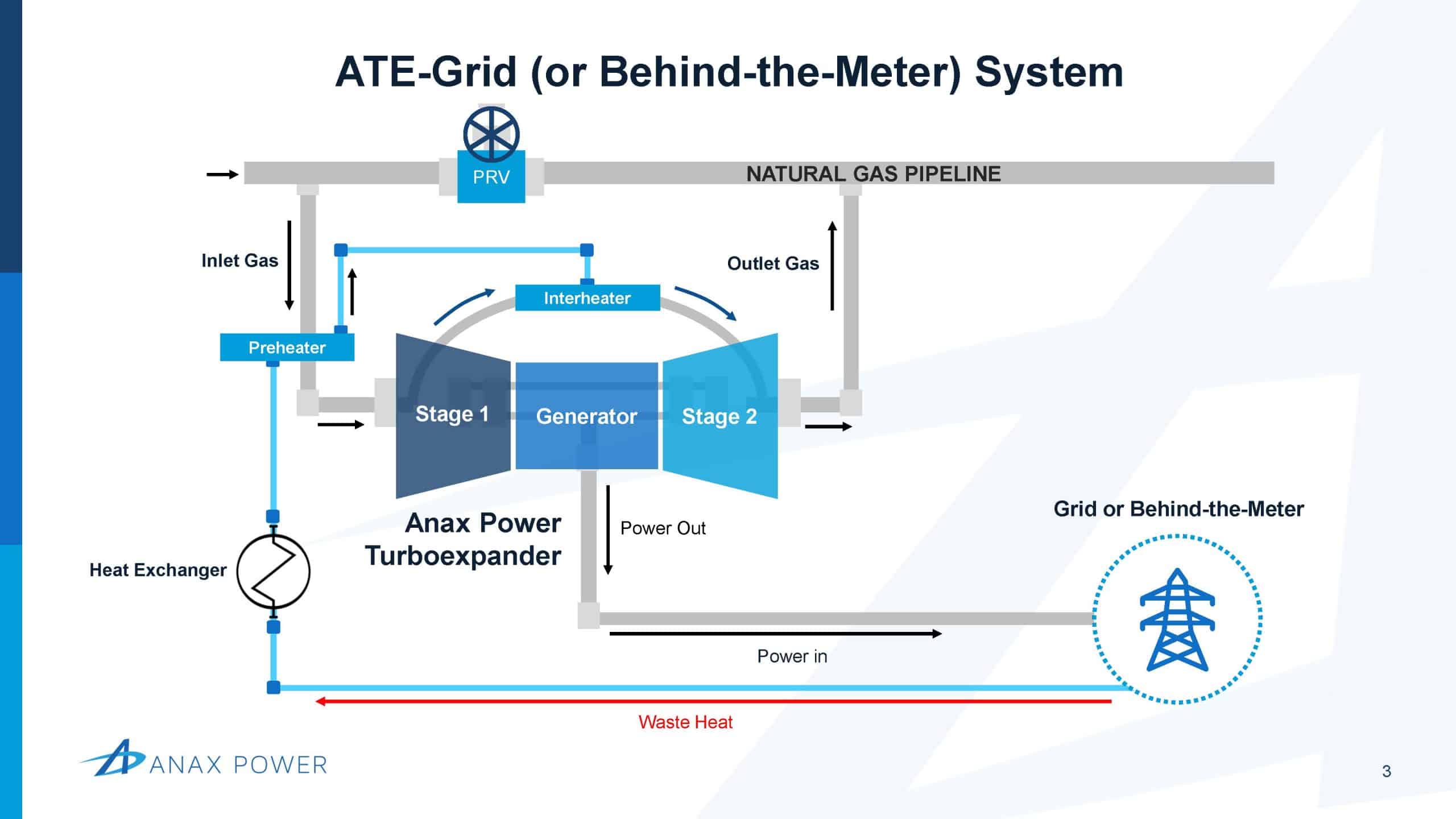
Power Grid
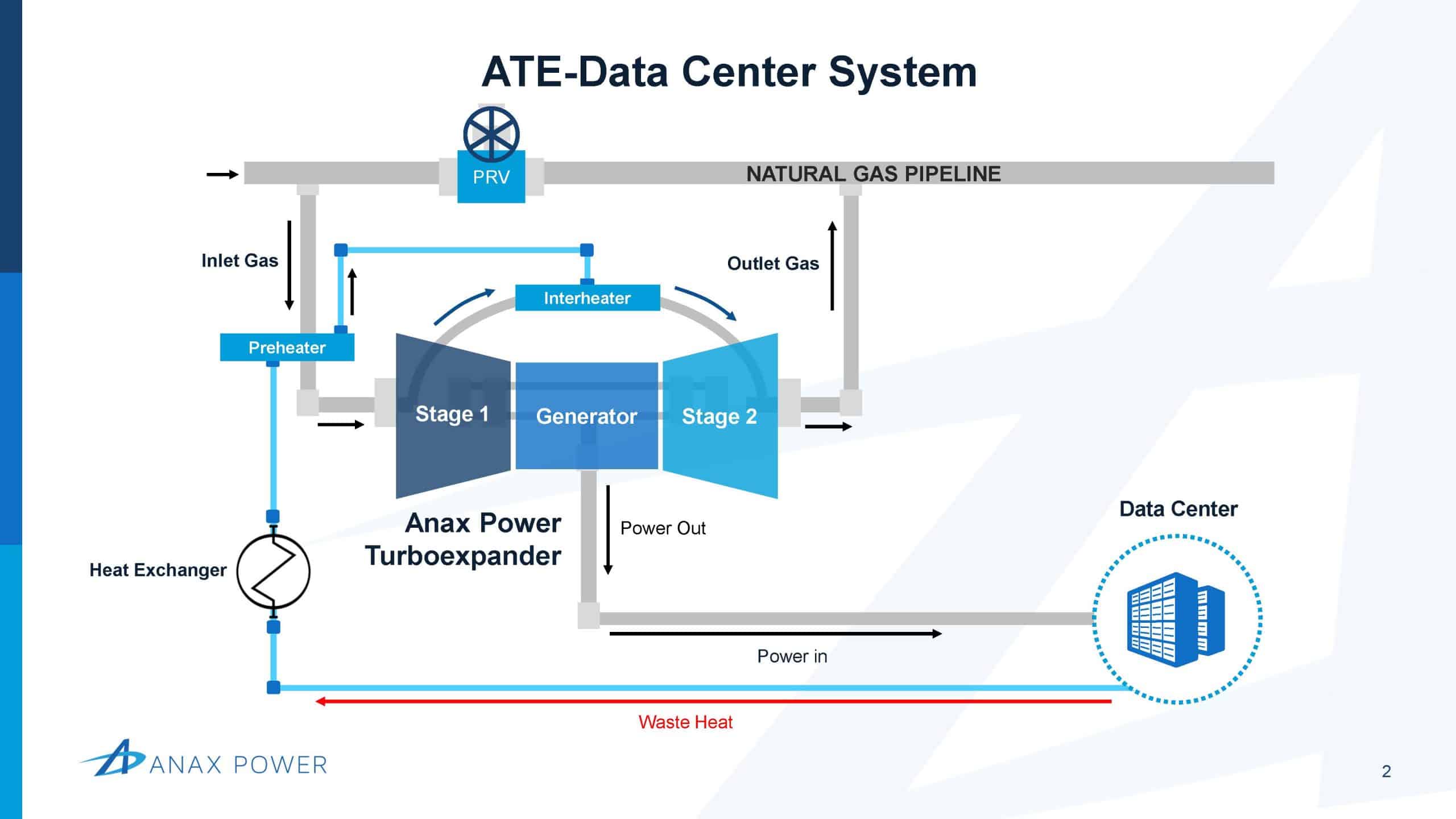
The most cost effective, efficient application for the ATE is a data center. Using a data center consumes the power behind-the-meter, avoids connecting to the grid, and circumvents burdensome regulatory procedures that can delay projects by years. The data center also generates valuable waste heat that offsets heat loss in the pressure letdown process.
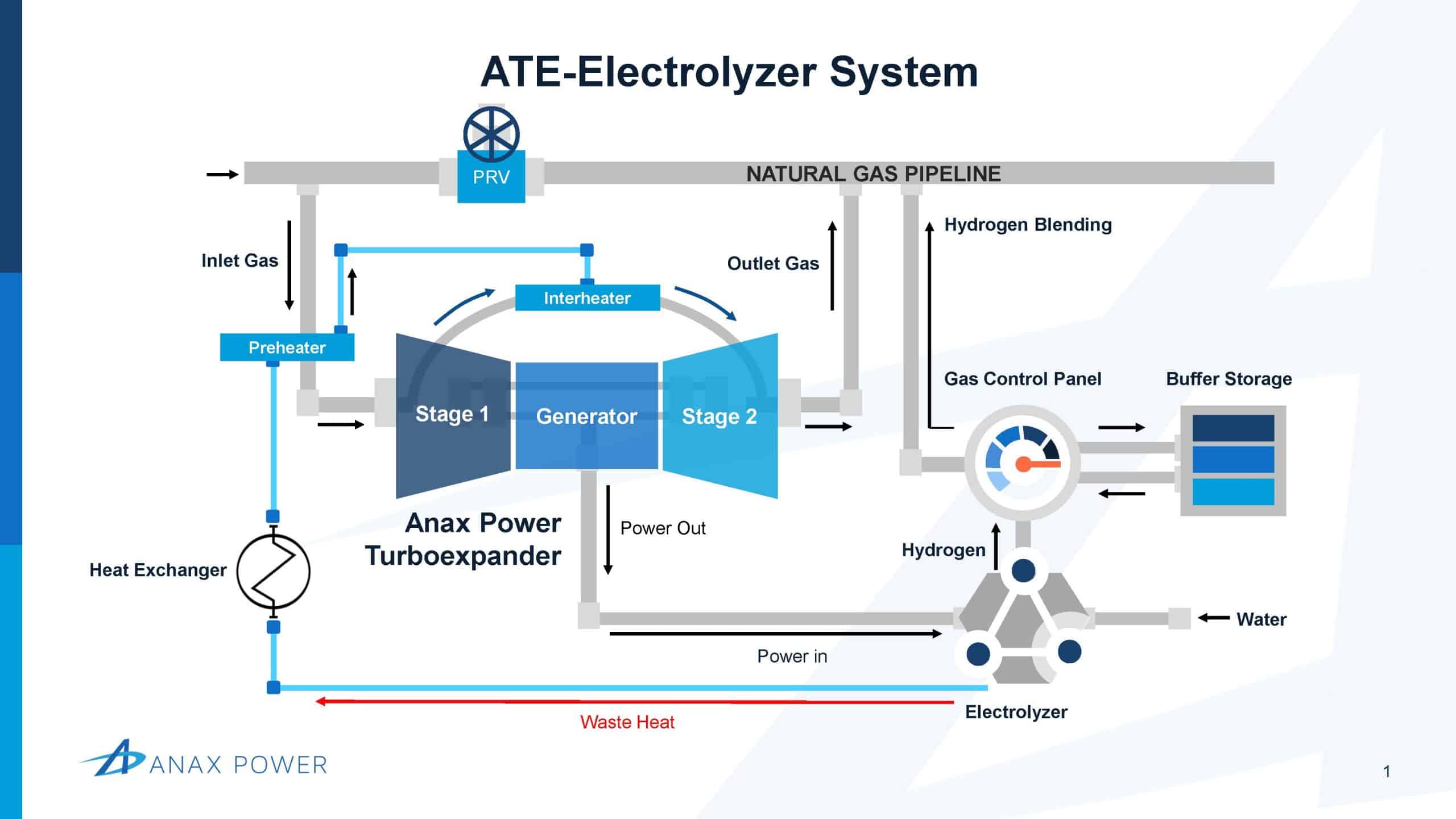
The ATE-Electrolyzer uses reliable, clean power to produce H2 for pipeline blending. Benefits include:
- Higher capacity factor (>90%) than other green H2sources like wind or solar (<40%).
- Eliminates project-killing storage and transportation costs for H2.
- Qualifies for same clean-energy incentives as traditional green H2.
- Distributed production allows for incremental H2blending to test the impact on pipelines up to 20%.
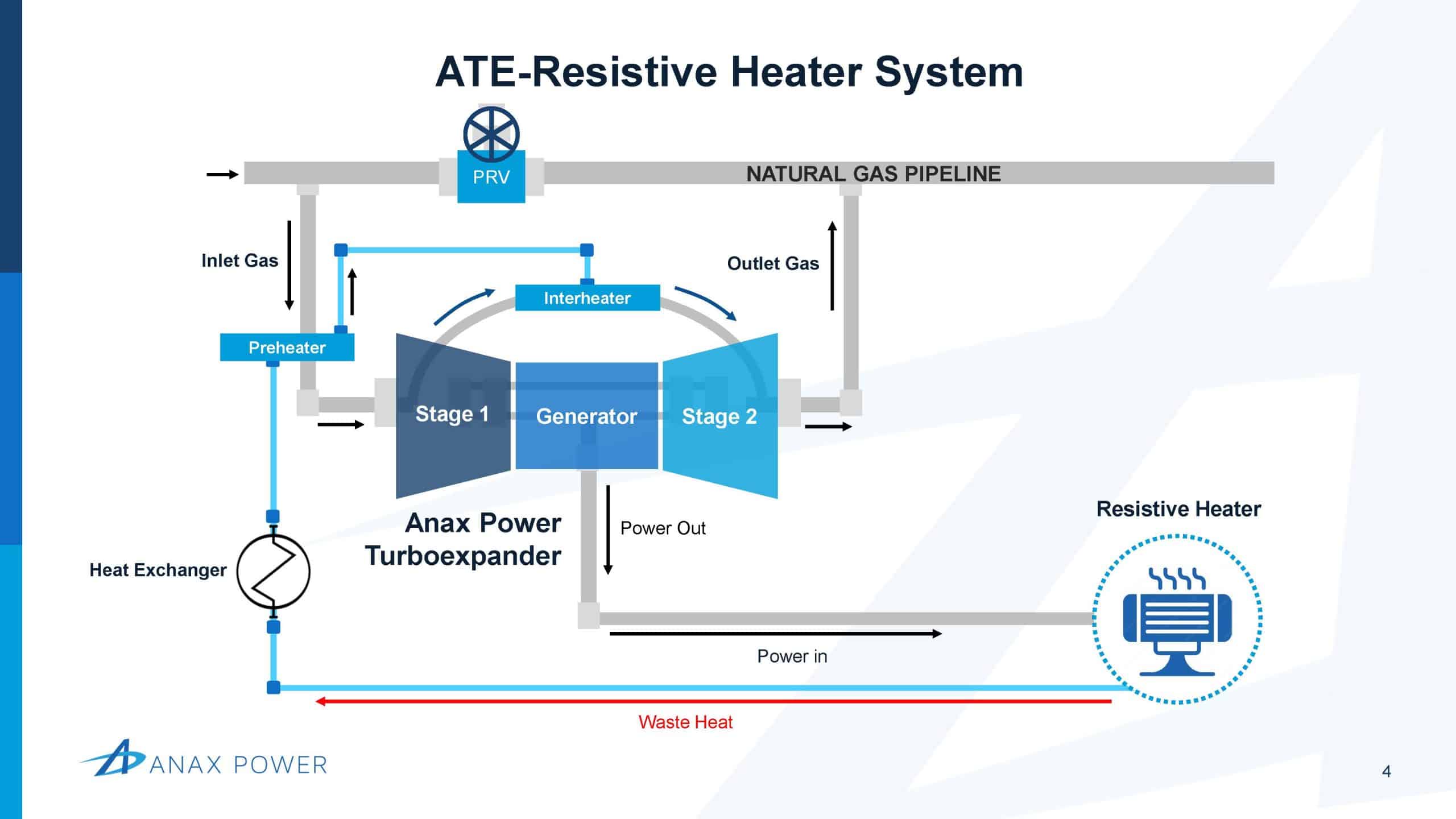
Consuming the ATE’s power in a resistive heater lets pipelines offset their scope 1 and scope 2 emissions at pressure regulating stations. These super-efficient heaters use clean electricity to offset heat lost in the gas expansion process and eliminate the need for inefficient, CO2-emitting, natural gas burning, line heaters.
ATE’s power can be run through a transformer and put onto a grid. While simple to execute, this use case carries regulatory and economic obstacles. It also does not provide useful waste heat like the other use cases.